Laser welding of copper and non-ferrous metals
Date:2024-01-15 Source: This website
Copper, gold and other non-ferrous metals
Existing industrial laser sources require more energy to process non-ferrous metals, such as copper, in batches. The development of blue diode lasers provides new possibilities for this situation. First, because copper and gold absorb blue light 7-20 times more than infrared light (see chart). Now, the first high-power diode laser more suitable for non-ferrous metal processing is available. Blue LDM diode lasers are more efficient in thin plate processing and have huge advantages.
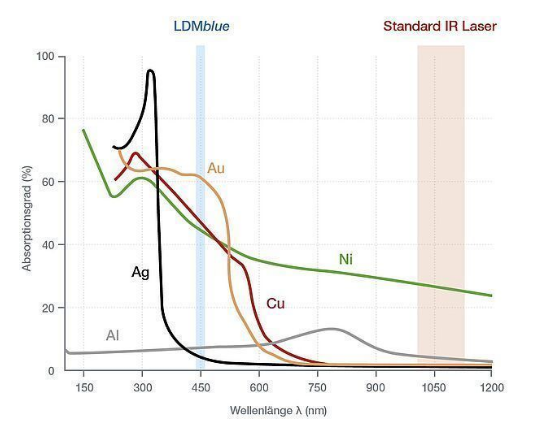
In addition to the high absorption rate of non-ferrous metals to blue light, the typical spot energy distribution of diode lasers also makes the melting of copper more stable and improves the quality of processed products. In addition, Laserline diode laser technology enables precise adjustment of laser power within milliseconds to better match the processing needs of customers. No matter what state the copper material is in before welding, the weld after welding with the blue diode laser is clean, smooth and has good electrical conductivity. There is little splash around the weld. Because the use of blue light does not require the material to be superimposed or filled at the weld, the material utilization rate is particularly high. In addition, when the blue laser is used for copper processing, the liquid copper has high wettability and is easy to weld. The process of blue laser heat conduction welding is highly controllable, and the connection of copper and other metal materials is realized for the first time. Even copper powder, copper sheet can also be welded with iron, aluminum and other materials. Among them, the weld and fillet welding of copper sheet have obtained good experimental results.
The energy consumption required by the blue laser on the welding of copper is 84% lower than that of the infrared laser, and even 92% lower on the welding of gold. This means that when the infrared laser takes 10 When welding copper or gold with a laser power of kW, using a blue laser requires only about 1 kW, or 0,5 kW of power.
The LDM laser platform, combined with high-quality lenses developed for the unique wavelengths of blue lasers, provides users with reliable system technology that is widely recognized in the industry. In addition, when the laser is integrated into the production system, there is no need to change many components when replacing other industrial lasers with blue lasers, and only need to replace the visual protection window and laser protection glasses of the workstation, so that it is protected against blue wavelengths to ensure the safety of the operator.

Laser welding technology of copper material
The blue laser realizes the controlled heat conduction welding process of copper and other non-ferrous metals with less hardness, and can easily process materials less than one millimeter. Thin metal sheet is easy to break and not easy to connect when processed by infrared laser. Materials can now be processed under controlled conditions with the help of blue lasers. The material can be melted along the weld with the help of a blue laser. The liquefied material melts and forms a weld after cooling, which is not only beautiful but also strong. This process is essentially similar to an infrared laser - Just using a different wavelength of laser.

Related news
- Introduction and application of laser tin wire welding
- Application and classification of laser soldering
- Jinghai laser large field laser welding machine helps battery module CCS module welding
- CO2 laser cutting machine dimming steps
- The difference between various kinds of laser welding machine
- Laser welding of medical endoscopes
- Application of picosecond laser cutting machine in glass industry
- The difference between coaxial vision, pseudo-coaxial vision and paraxial vision
- Introduction to precision ceramic laser processing equipment
- Introduction of standard automation equipment for large format glass laser cutting


































 Building 4, 88 Wubian Avenue, Wujiang District, Suzhou
Building 4, 88 Wubian Avenue, Wujiang District, Suzhou